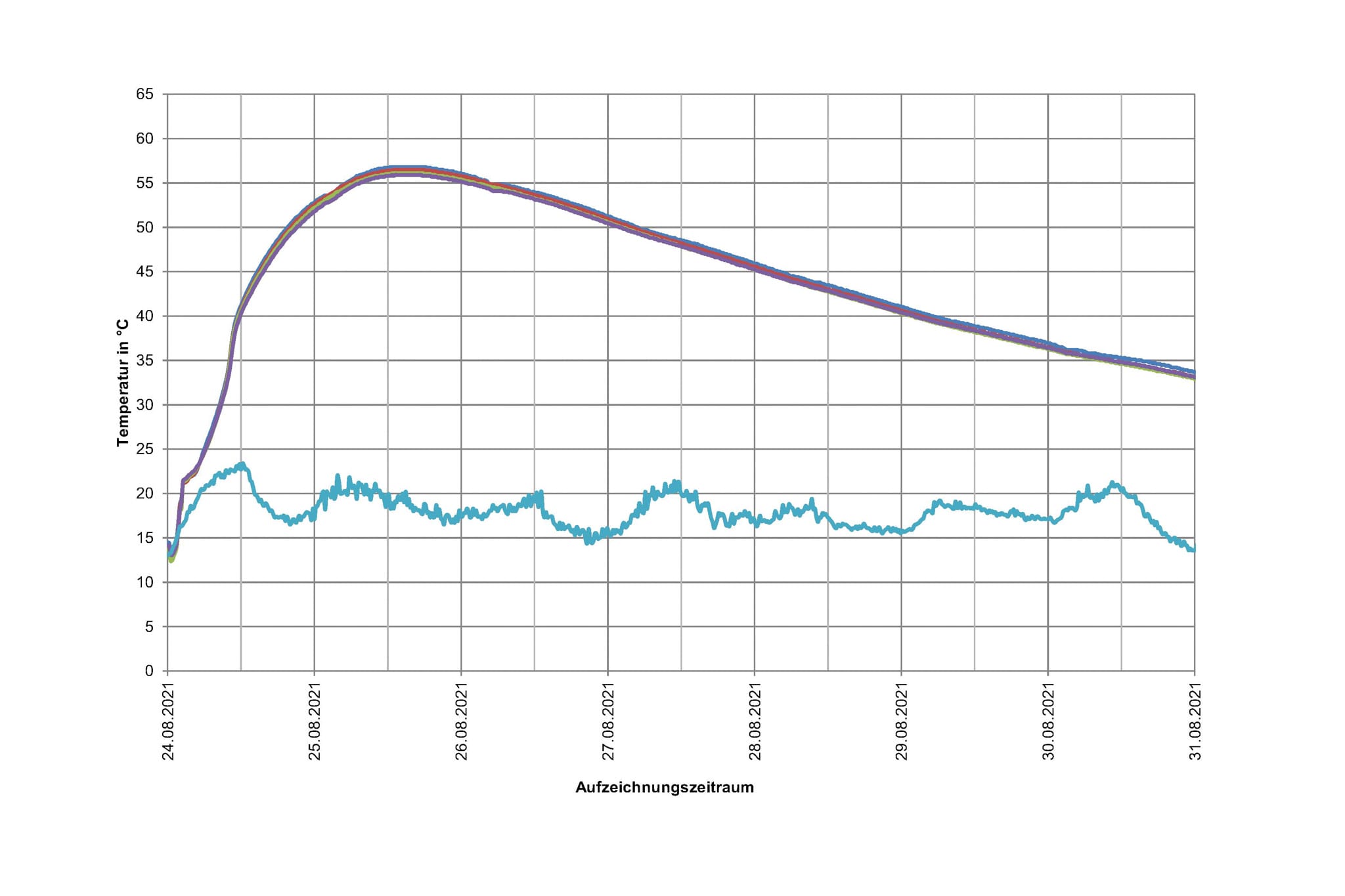
The release of hydration heat that accompanies the hardening of concrete can cause a significant increase of the temperature in the component, especially in the case of bulky components. This gives rise to pressure forces that can cause cracks, if they exceed the tensile strength of the concrete, affecting its durability. Web-based data loggers (remote retrieval) allow for simultaneous long-term measuring and monitoring of multiple measuring points in mains or battery-powered operation.
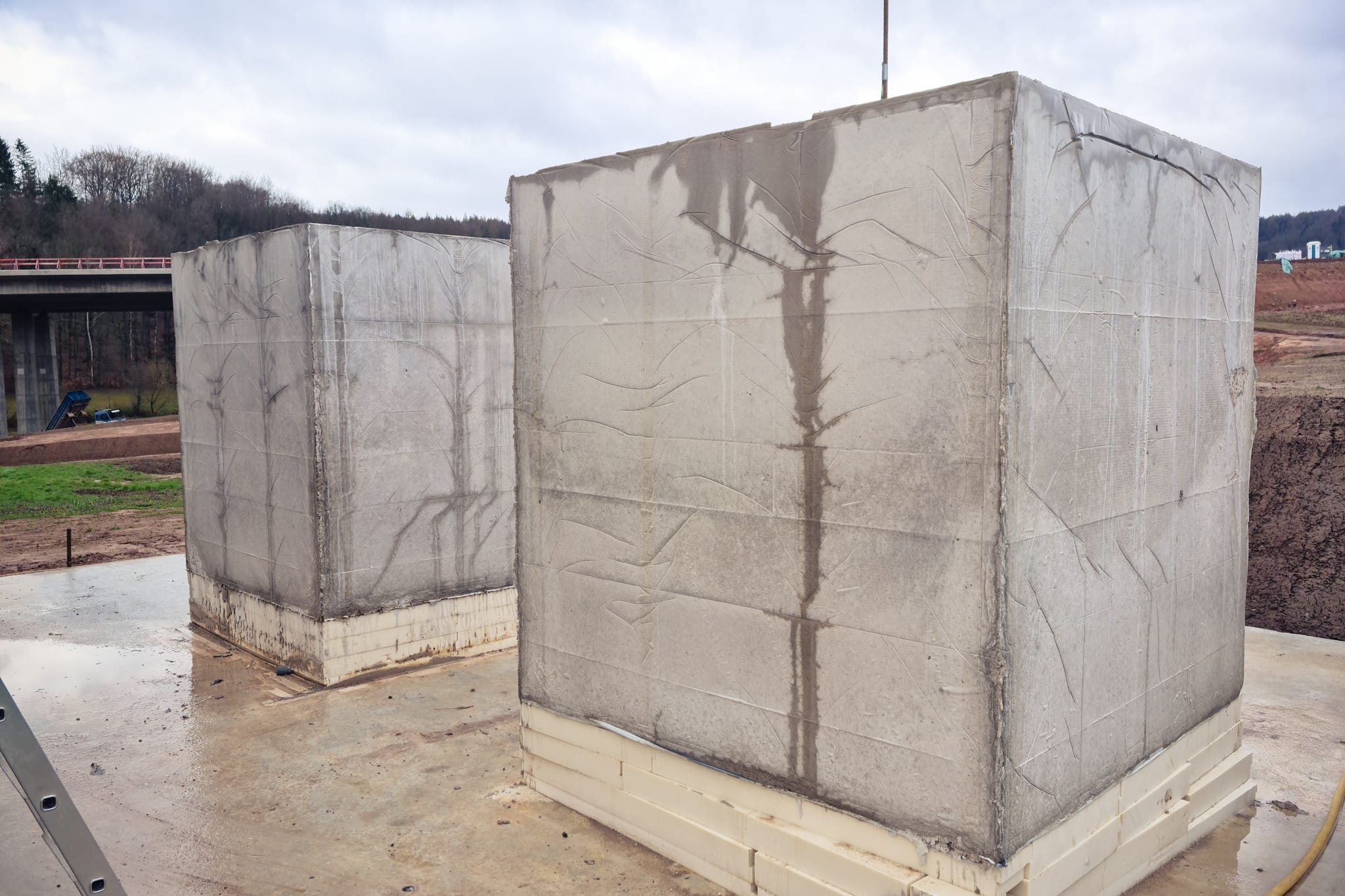
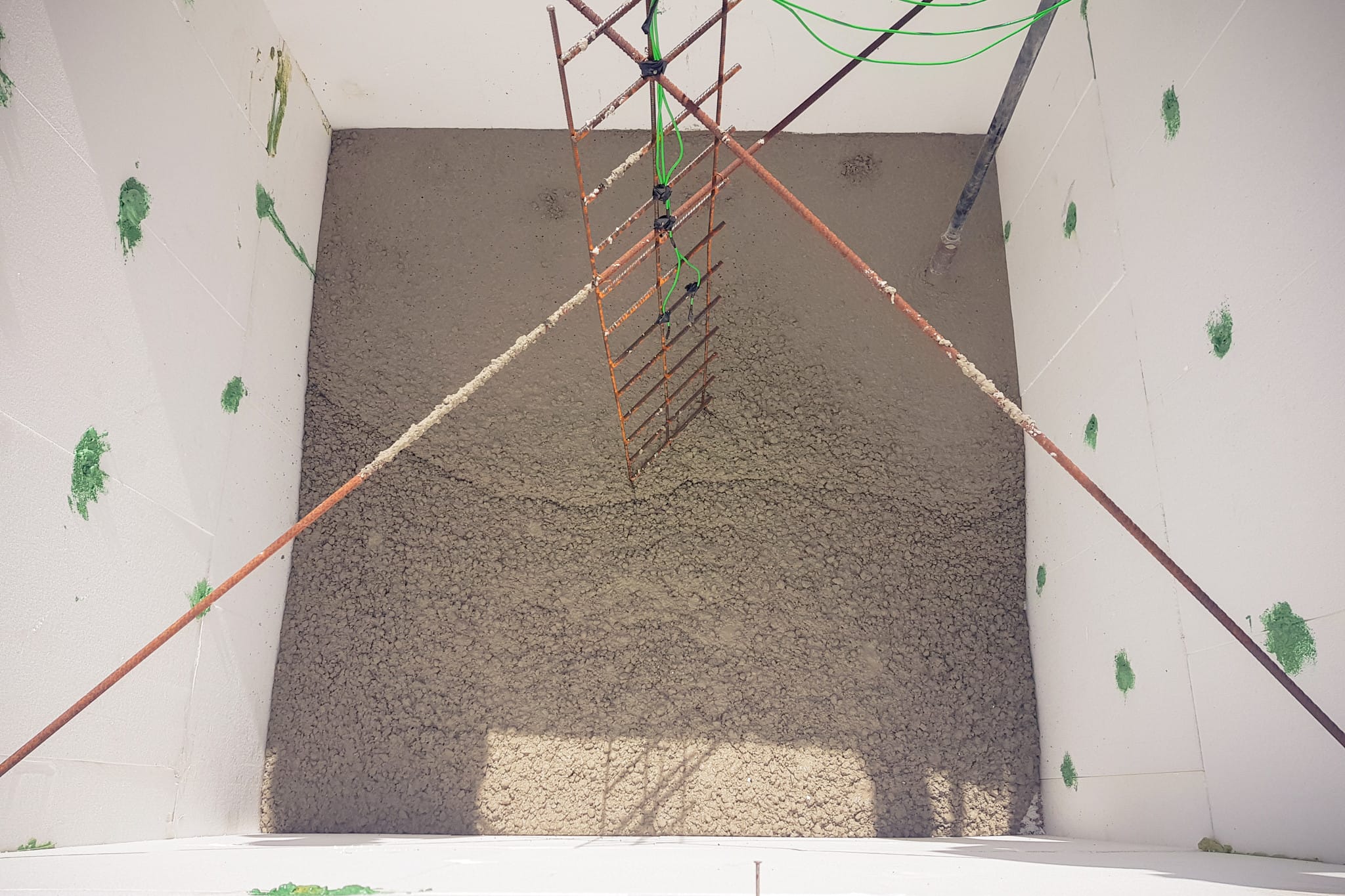
The temperature increase can, for example, be recorded via an on-site test for concretes according to ZTV-W LB 215. The temperature is measured on large-format concrete blocks with an edge length of 2 m that are equipped with heat insulation. The applicable testing conditions are outlined in ZTV-W LB 215. Quasi-adiabatic conditions can therefore be assumed for these measurements. At the same time, manufacture-related effects from concrete production, transport and installation are simulated.
While the test is carried out on the concrete block, the concrete temperature is recorded for a period of at least seven days and analysed.
More projects
C³ – Carbon Concrete Composite
Our tasks included experimental verification concerning the creep behaviour in chemically reactive…
Fire resistance testing of a wall/ceiling connection made of solid wood elements
MFPA Leipzig GmbH developed a corresponding test set-up to verify smoke tightness (in relation to…
Load-bearing safety testing on bridge structures
In order to investigate the load-bearing capacity of the Leipzig Klinger Bridge in , a load test…